An In-Depth Look at How Garage Doors Are Made In Minnesota
Apple Valley Garage Door Repair has assembled a detailed manufacturing walkthrough that reveals how a typical Minnesota residential garage door is built—from raw metal sheets to a finished, balanced unit ready for installation as part of a garage door replacement or new build in Minneapolis area. Apple Valley Garage Doors are designed to handle our harsh winters and hot summers without cracking, breaking, or warping.
This guide follows each stage of the process, explains the reasoning behind material choices and construction techniques, and offers practical maintenance and selection advice for homeowners and professionals in the Twin Cities.
What makes a modern garage door a good fit for Harsh Minnesota weather?
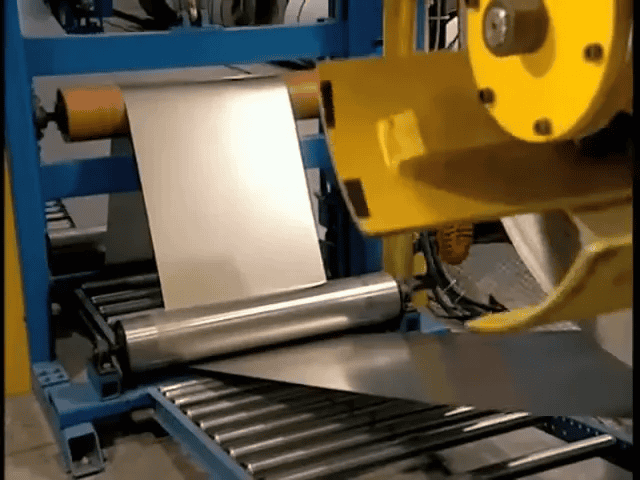
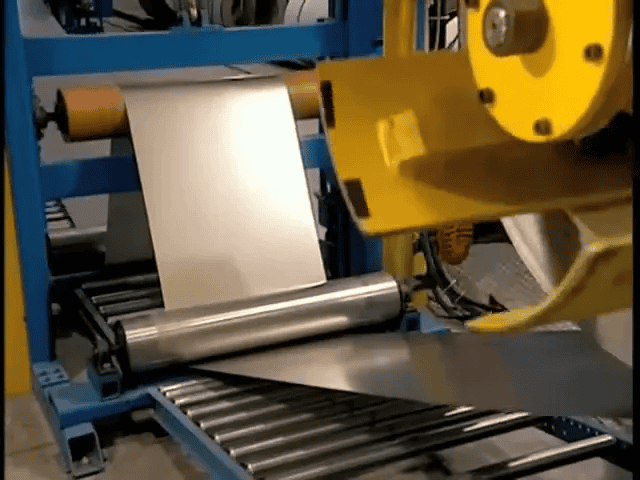
A standard residential garage door typically consists of four interlocking panels, engineered to withstand weather, provide insulation, and operate smoothly for years. These panels begin as continuous metal sheets—usually aluminum or steel—chosen for strength, durability, and corrosion resistance.
A combination of surface treatments, reinforcements, insulation, and hardware integration transforms those sheets into a functional door that balances aesthetics, performance, and safety.
Materials and surface finishing
The surface that faces outward receives a baked-on polyester coat, a finish selected for durability, UV resistance, and the ability to match a wide range of exterior styles. The polyester paint is flexible—an important characteristic since panels must bend at the joints during operation. Because the paint stretches with the metal when the door flexes, it resists cracking and maintains an even appearance over time, even as seasons change year after year in Apple Valley, MN.
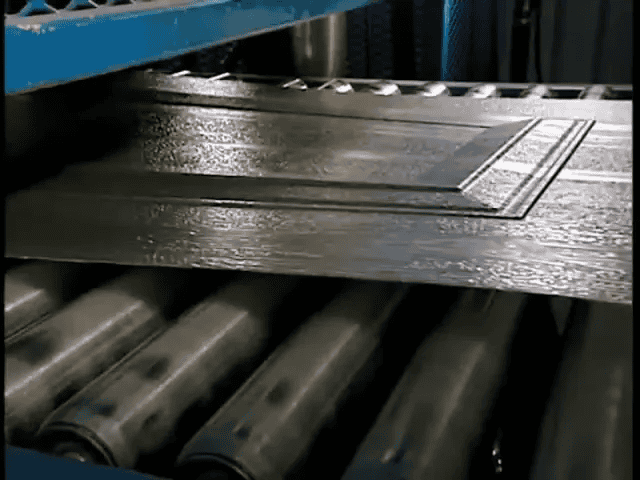
Before or during finishing, the sheet can pass through rollers that imprint textures such as simulated wood grain. After texturing, a press creates the decorative design—raised rectangles for a classic look, horizontal stripes for a modern aesthetic, or a smooth surface for minimalist designs. These surface options allow homeowners to customize the door’s appearance without sacrificing the structural characteristics that make it reliable.
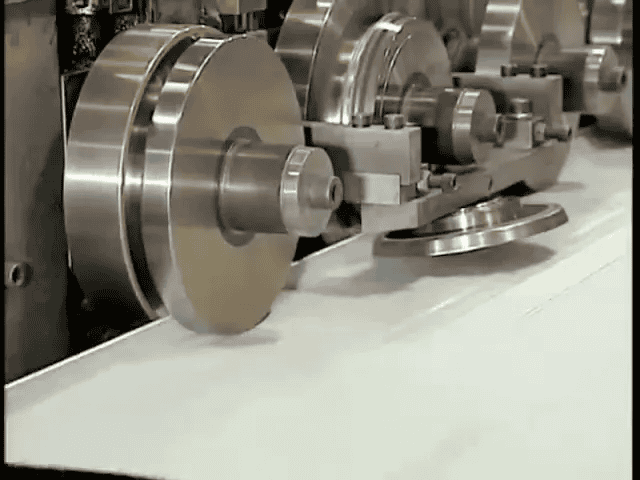
Cutting, forming, and creating panel joints
Production lines typically feed long continuous sheets through automated cutters that slice them to the width of individual garage door panels. Another machine folds the edges to create one-and-a-half centimeter joints—these are the hinge interfaces where adjacent panels attach.
The precision of these folds determines how snugly the panels fit together, which affects both the look of the door and its ability to seal against Apple Valley, Minnesota weather and drafts.
Because the painted finish is elastic, those folded edges can flex during operation without damaging the coating. This engineered flexibility reduces long-term maintenance needs like repainting or touch-ups, while preserving the mechanical integrity of the joint.
Reinforcement and hardware preparation
On the interior face of each sheet, workers or automated equipment hot-glue metal plates in strategic locations. These plates function as internal anchors for lift handles, hinges, and the brackets that hold the electric opener mechanism.
The reinforcement plates prevent the base metal from deforming when screws or bolts are tightened during installation, ensuring reliable attachment points that can bear repeated stress.
At the same time, the production line drills small holes through the interior cavity of the panel. These holes are used later to inject insulation and to allow the expanding material to be introduced in a controlled way so it reaches the entire hollow space. Clearly marking the attachment points—often with colored stickers or dots—helps installers position hinges and handles accurately in the field.
Two sheets slide together to form each panel, and the ends are closed off with pine blocks. These wooden end caps help seal the hollow cavity, preventing water and cold air from penetrating the panel ends and improving overall thermal performance.
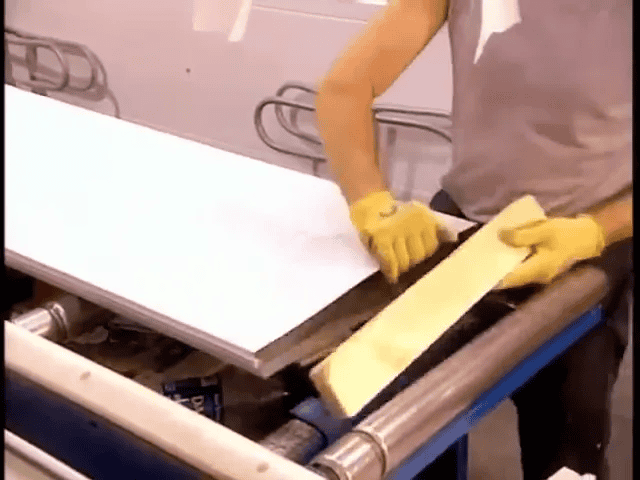

Labeling, packing cues, and temporary fixtures
Before insulation is introduced, panels receive stickers that provide installation, maintenance, and safety information. Installers also place orange dot markers to indicate where hinges and lift handles should be screwed in. These simple visual cues reduce the chance of incorrect installations and speed up field assembly.
To stabilize panels through the injection process, aluminum bars clamp onto the long edges. These bars keep the panel square and prevent bulging while the foam fills and expands. Once the insulation cures and forms a rigid core, the bars are removed and the panel continues down the line for finishing.
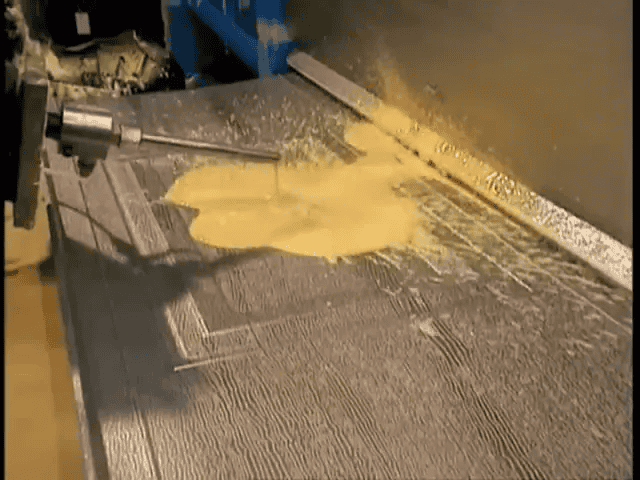
Insulation: Polyurethane foam and why it’s used in Apple Valley, Minnesota
Insulation is injected into the hollow interior cavity through the pre-drilled access hole. Polyurethane foam is commonly used because it expands to fill irregular spaces, creates an effective thermal barrier, and cures into a rigid core that increases the panel’s stiffness. As the foam expands, it bonds to the interior surfaces and eliminates air pockets that would otherwise reduce energy performance. This helps keep the garage warmer during the winter months and cooler during the summers.
Polyurethane is one of the lightest commercial insulation materials, so it adds minimal weight to the panel while dramatically improving its R-value (resistance to heat transfer). This combination of light weight and stiffness helps keep the door manageable for both manual and automated openers. After curing, the interior looks like a solid composite core rather than a hollow space, which enhances strength and dampens noise when the door moves.
The injection process often occurs on a rotating carousel system that feeds panels to the injection station in a steady sequence. Automated controls meter the foam components and monitor expansion to ensure consistent density and coverage across every panel produced.

Seals, weatherstripping, and water protection for Twin Cities weather
Once insulation is cured and temporary clamps are removed, workers install weather seals. A key component is the rubber seal applied to the bottom panel; it prevents cold air, rain, snow, and debris from entering the garage under the door. Side and top seals are also used at the installation site to create a continuous barrier around the door perimeter.
Proper weatherstripping extends the life of stored items, reduces energy bills, and prevents water damage to the garage interior. For climates like ours in Minnesota with heavy precipitation or significant temperature swings, selecting the right seal material and ensuring tight installation are critical steps toward long-term performance.
Windows and natural light options
Some garage door models include windows to admit natural light and improve curb appeal. To add windows, workers use a high-speed router to remove rectangles in the panel surface where glass will be fitted. The window assemblies typically use double-sealed units—two thermal panes separated by an aluminum spacer—to reduce heat transfer and minimize condensation.
Framing around the glass is usually made from PVC, a synthetic resin selected for its color stability and resistance to discoloration over time. PVC frames also help prevent water intrusion and maintain a tight seal between the glass and the panel. Available frame colors and glass styles provide homeowners with customization options that match the home’s exterior.
Packing, quality control, and shipping
After assembly, each door set is boxed with the required installation hardware, including hinges, rollers, cables, bracketry, and mounting instructions. Boxes are weighed to ensure no part is missing—a simple but effective quality control check that reduces installation delays and warranty claims.
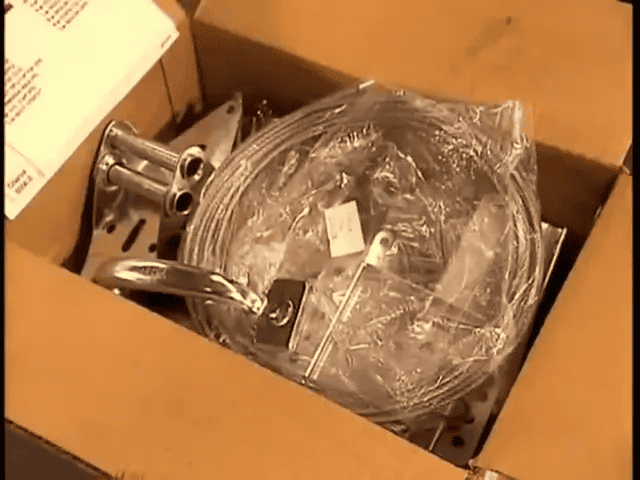

Manufacturers may also apply a final inspection to verify surface finish, hardware placement, and the integrity of the weather seals. Panels are then palletized and shipped to dealers, distributors, or direct-install teams.
On-site installation and balance
At the installation site, technicians attach the door panels at the joints using hinges and fasteners. A crucial part of installation is installing a spring system that counterbalances the door’s weight. Properly calibrated springs allow the door to move smoothly along tracks and permit easy manual operation in the event of power loss or opener failure. When correctly installed, the door should be balanced so well that it can be lifted or lowered using just two fingers—evidence of proper spring tension and hardware alignment.
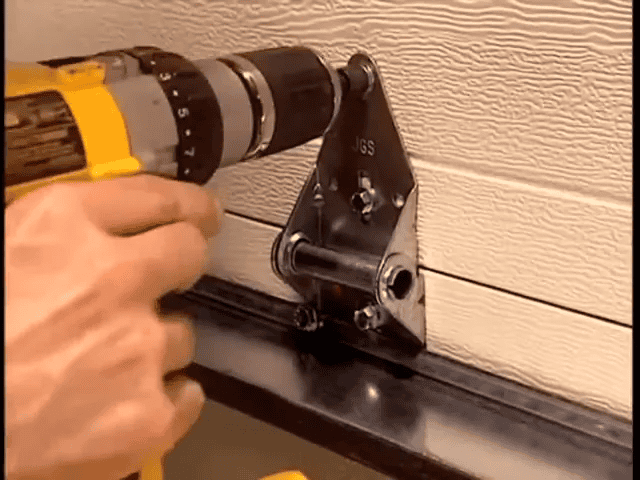

Balance also reduces strain on the opener motor and extends the life of moving parts like rollers and tracks. A balanced door lowers the frequency of garage door repairs and helps maintain consistent performance year after year.
Maintenance best practices
Routine maintenance keeps doors operating safely and efficiently for Minnesota homeowners. Simple, periodic tasks can prevent small issues from becoming major repairs. For example, lubricating moving parts like hinges, rollers, and springs reduces friction and wear. In fact, many professionals emphasize that lubricating your garage door is best for a longer lifetime—consistent application of the right lubricant helps components move freely and reduces the risk of early failure.
- Inspect weather seals seasonally and replace if cracked or rigid.
- Check balance and spring tension annually; if the door is heavy or unbalanced, contact a qualified technician.
- Clean and inspect windows, frames, and finishes to address moisture and discoloration early.
- Test safety reversal mechanisms on electric openers monthly to ensure compliance with modern safety standards.
Painting, refinishing, and aesthetic maintenance
Homeowners often consider repainting to refresh the look of a garage door. When thinking about painting a garage door, it’s important to consider the door’s original finish and the material of the panels. Baked-on polyester and powder-coat finishes are durable, but when a new color or texture is desired, appropriate surface preparation and paint selection are essential. Using a paint recommended for metal exteriors and following proper priming and curing practices will prevent peeling and uneven coverage. If the door has integrated insulation or specific warranties, homeowners should consult the manufacturer or a qualified installer before repainting to avoid voiding warranty terms.
Common garage door repairs and when to call a pro
Even with excellent manufacturing and maintenance, doors still require repairs from time to time. Typical issues include broken springs, frayed cables, misaligned tracks, worn rollers, and malfunctioning openers. While some minor adjustments—like tightening loose screws or replacing seals—can be DIY tasks for a handy homeowner, critical elements such as spring replacement or cable adjustments present safety risks and should be handled by trained technicians.
The phrase garage door repairs covers a wide range of interventions, from simple part swaps to full door replacements. For complicated or hazardous work, contacting a reputable local service—such as Edina Garage Door Repair or Apple Valley Garage Door Repair—ensures the job is done safely and according to manufacturer specifications. Professionals have the tools, training, and factory parts required for reliable, code-compliant repairs.
Choosing the right door for your Twin Cities home
Selecting a garage door for your Minneapolis home involves trade-offs among cost, insulation value, appearance, and maintenance. Key factors to weigh include:
- Material: Steel is durable and economical; aluminum is lightweight and corrosion-resistant; wood provides natural beauty but requires more upkeep.
- Insulation (R-value): Homes attached to garages benefit from higher R-value doors to reduce heat transfer and conserve energy.
- Window options: Placing windows high keeps privacy while providing light; double-sealed thermal panes reduce heat loss.
- Finish: Textures and profiles (raised panels, horizontal lines, smooth faces) should complement the home’s architecture.
- Hardware and opener compatibility: Ensure the door’s weight and balance match the opener’s specifications and that hardware mounting points align with reinforcements.
When in doubt, consulting a professional installer helps homeowners choose a model that meets climate demands, style preferences, and maintenance expectations.
Sustainability and lifecycle considerations
Modern manufacturing emphasizes both product longevity and environmental considerations. Steel and aluminum are highly recyclable, and manufacturers often design doors for long service life to reduce lifecycle impacts. Insulation choices matter not only for energy efficiency in the home but also for their environmental footprint. While polyurethane offers excellent thermal performance and light weight, homeowners interested in greener alternatives should discuss options like recycled-core panels or alternative foams with their supplier.
Summary and practical takeaways
From the initial choice of metal sheet to the final balancing of springs, the manufacturing process for residential garage doors blends material science, mechanical engineering, and quality control. Reinforcement plates and precise joints ensure that hardware remains secure. Injected polyurethane provides a lightweight, rigid core that improves thermal performance without increasing weight. Weather seals and PVC-framed windows protect against the elements while offering design flexibility. Thorough packaging and simple field markers reduce installation errors and speed up the process for technicians on site.
For homeowners, regular maintenance—especially lubricating moving parts—reduces the need for extensive garage door repairs and extends service life. If advanced maintenance or repair is required, reputable services such as Apple Valley Garage Door Repair or local pros should be engaged, particularly for high-risk tasks like spring replacement or cable work.
FAQs:
Why is polyurethane used for insulation inside garage door panels for Minnesota weather?
Polyurethane foam expands to fill the panel cavity, creating a rigid, continuous core that improves the door’s R-value and structural stiffness. It is also very light, which means the door remains easy to operate and puts less strain on opening mechanisms.
How does the painted finish survive panel bending at the joints?
The baked-on polyester paint used on finished panels is elastic and stretches slightly with the metal during bending. This prevents cracking or flaking at folded edges and joints, preserving the door’s appearance over time.
What routine maintenance keeps a garage door lasting longer?
Regular inspection of seals, rollers, and tracks, testing of safety reversal mechanisms, and lubricating moving parts are key steps. In particular, lubricating your garage door is best for a longer lifetime because it reduces friction and wear on components.
Can Minneapolis homeowners repaint their garage door?
Yes, but painting a Minnesota garage door requires consideration of the existing finish, material, and manufacturer warranty. Use the right primers and exterior metal paints and verify whether the new finish will impact the door’s balance or warranty terms.
What are common garage door repairs that require a professional in minnesota?
Springs and cables are the most dangerous components and should be serviced only by trained technicians. Problems like misaligned tracks, broken springs, or frayed cables typically require professional tools and expertise to fix safely and correctly.
Do windows reduce a door’s insulation performance?
Windows can reduce insulation performance if they are single-pane or poorly sealed. However, double-sealed thermal panes with aluminum spacers and well-designed PVC frames minimize heat transfer and provide good thermal performance while allowing natural light.
Who should homeowners call for troubleshooting and repairs?
Qualified local service providers should handle complex repairs. For example, Apple Valley Garage Door Repair is an example of a professional service that can manage spring replacements, opener issues, and full door installations safely and in accordance with local codes.
How important is door balance and how is it tested?
Door balance is crucial for smooth operation and long-term reliability. A properly balanced door can typically be lifted or lowered with only two fingers when springs are correctly tensioned. If the door is heavy to move or the opener struggles, balance should be checked and adjusted by a professional.
What should be included in a pre-installation inspection?
Inspect the opening for plumb and level conditions, verify the structure’s ability to support the door and opener, check for adequate clearance for tracks and springs, and confirm that reinforcements and attachment points match the door’s hardware layout. Ensuring these factors ahead of installation prevents delays and improper mounting.
Closing thoughts
The manufacturing process for residential garage doors reflects a careful balance of materials engineering, practical design, and quality control. From baked-on polyester finishes and textured surfaces to injected polyurethane cores and reinforced attachment points, every step aims to deliver a product that is attractive, energy-efficient, and dependable. Homeowners should consider product specifications, climate demands, and maintenance commitment when selecting a door, and always prioritize safety by hiring professionals for complex garage door repairs. When professional service is required, companies such as Edina Garage Door Repair or Apple Valley Garage Door Repair provide the expertise needed to keep the door operating smoothly for years to come.